COCA IS NOT COCAINE
Group 4 project
Amazonas 2014
COCAINE (-)
the other (and dark) side of the coin
-
Cocaine is a crystalline tropane alkaloid that is obtained from the leaves of the coca plant.
-
The name comes from "coca" and the alkaloid suffix "-ine", forming "cocaine".
-
It is a stimulant, an appetite suppressant, and a nonspecific voltage gated sodium channel blocker, which in turn causes it to produce anesthesia at low doses.
-
Biologically, cocaine acts as a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor, also known as a triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI).
-
It is addictive due to its effect on the mesolimbic reward pathway.
-
It is strongly more dangerous than other CNS (central nervous system) stimulants, including the entire amphetamine drug class.
-
At high doses due to its effect on sodium channels, as blockade of Nav1.5 can cause sudden cardiac death.
-
It is called "the caviar of street drugs," (because of its high price).
-
It is seen as the status-heavy drug of celebrities, fashion models, and Wall Street traders.
-
It has powerful negative effects on the heart, brain, and emotions.
Cocaine and Crack
Cocaine is a purified extract from the leaves of the coca bush. There are different chemical processes that produce the two main forms of cocaine:
-
Powdered cocaine: commonly known on the street as "coke" or "blow,” dissolves in water. Users can snort or inject powdered cocaine.
-
Crack cocaine: commonly known on the street as "crack" or "rock,” is made by a chemical process that leaves it in its "freebase" form, which can be smoked.
What’s being high on cocaine?
Smoking or injecting cocaine has nearly instantaneous effects. Rapid absorption through the nose makes snorting cocaine nearly as fast. Whatever the method, it quickly enters the bloodstream and travels to the brain.
In the brain, cocaine interferes with the neurotransmitters that nerves use to communicate with each other. Cocaine blocks norepinephrine, serotonin, dopamine, and other neurotransmitters from being reabsorbed. This causes euphoria or feeling "high."
The “good” side of being high:
-
An increasing sense of energy and alertness
-
An extremely elevated mood
-
A feeling of supremacy
And there are the bad effects:
-
Irritability
-
Paranoia
-
Restlessness
-
Anxiety
You know someone’s high on coke when:
-
Their pupils are dilated
-
They show high levels of energy and activity
-
Excited, exuberant speech
Physiological Effects of Cocaine
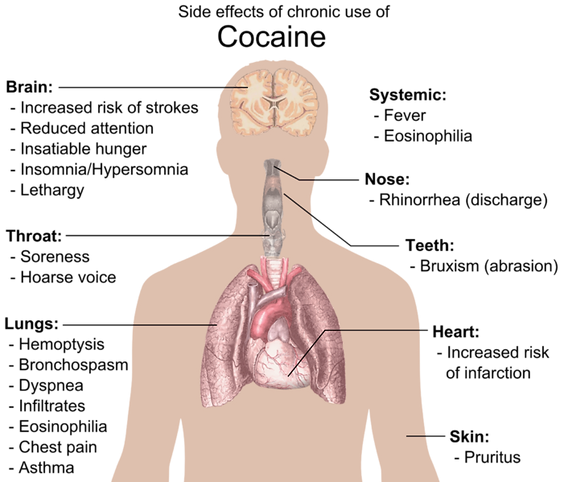
Cocaine’s strongest activity is on the brain, but as it travels through the blood, it affects the whole body. Things that happen in the body:
-
Heart: cocaine is bad for the heart; it increases heart rate and blood pressure while constricting the arteries that supply blood to the heart. The result can be a heart attack, even in young people without heart disease. Cocaine can also trigger a deadly abnormal heart rhythm called arrhythmia.
-
Brain: cocaine can constrict blood vessels in the brain, causing strokes. This can happen even in young people without other risk factors for strokes. Cocaine causes seizures and can lead to bizarre or violent behaviour.
-
Lungs and respiratory system: snorting cocaine damages the nose and sinuses. Regular use can cause nasal perforation. Smoking crack cocaine irritates the lungs and in some people permanent lung damage.
-
Gastrointestinal tract: cocaine constricts blood vessels supplying the gut, which results in oxygen starvation that can cause ulcers, or even perforation of the stomach or intestines.
-
Kidneys: cocaine can cause sudden kidney failure through a process called rhabdomyolysis. In people with high blood pressure, regular cocaine use can accelerate the long-term kidney damage caused by high blood pressure.
-
Sexual function: although cocaine has a reputation as an aphrodisiac, it may make you less able to finish what you start. Chronic cocaine use can impair sexual function in men and women. In men, cocaine can cause delayed or impaired ejaculation.

![drug-abuse3[2].jpg](https://static.wixstatic.com/media/1feb03_d950841154e54eb29cd8ce6f71bc9909.jpg/v1/fill/w_700,h_438,al_c,q_80,enc_avif,quality_auto/1feb03_d950841154e54eb29cd8ce6f71bc9909.jpg)


Gabriela Oliveros G.
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
How cocaine works in the brain